Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved from being a peripheral add-on to becoming a core enabler of enterprise innovation. Within the SAP ecosystem, AI now drives automation, decision intelligence, predictive analytics, and user-centric experiences.
To integrate AI into complex enterprise environments like SAP S/4HANA, organizations typically adopt one of two architectural models:
- Embedded AI (within the SAP core)
- Side-by-Side AI (externally orchestrated and connected)
Each model has its strengths, trade-offs, and ideal use cases — and understanding this distinction is essential for architecting intelligent, scalable SAP solutions.
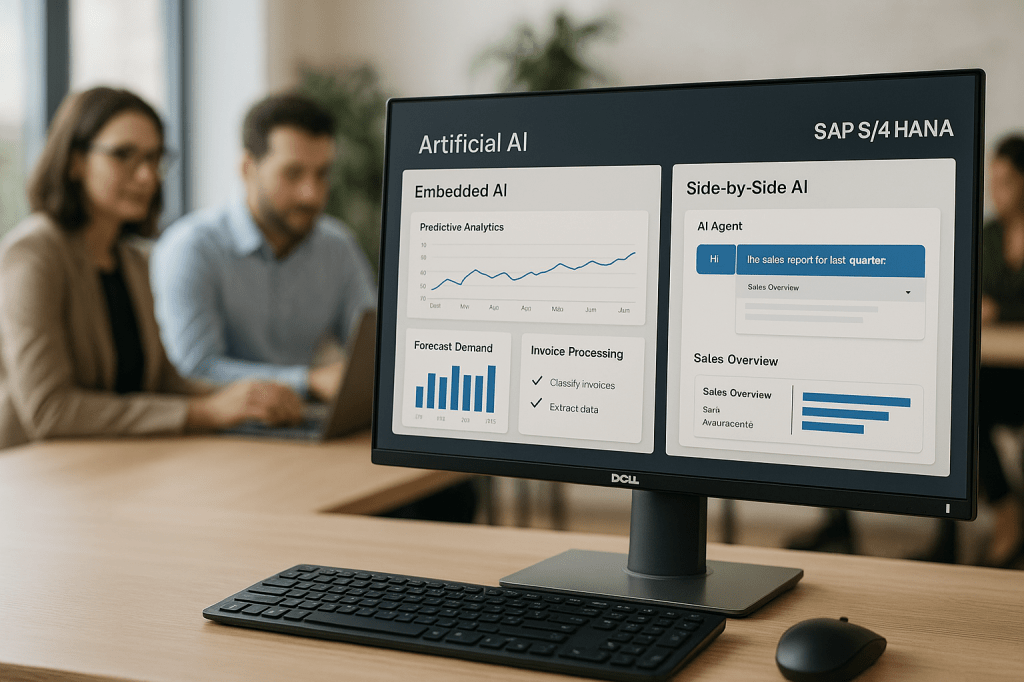
1. Two Models of AI Provisioning in SAP S/4HANA
Embedded AI (In-System)
In this model, AI capabilities are natively built into the SAP application layer or in-memory database (SAP HANA). These AI services operate in real-time, embedded directly into transactional workflows.
Key Characteristics:
- Tight integration with core business logic
- Real-time inference and automation
- No need for external orchestration
Examples:
- Predictive MRP
- Intelligent Invoice Matching
- Machine Learning in SAP HANA via PAL/AFL libraries
Side-by-Side AI (Externalized)
In contrast, side-by-side AI runs outside the SAP core — on platforms such as SAP BTP, Azure, or AWS — and connects via APIs, events, or messaging frameworks.
Key Characteristics:
- High scalability (e.g., GPU/LLM support)
- Easier experimentation and model iteration
- Can combine SAP and non-SAP data
Use Cases:
- Generative AI assistants for customer service
- Predictive models consuming IoT + SAP data
- LLM-powered document summarization and chatbots
2. Why This Distinction Matters
While both approaches are essential, they differ significantly in terms of architecture, flexibility, and implementation effort:
| Dimension | Embedded AI | Side-by-Side AI |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Depth | Deep (within SAP core) | Loosely coupled |
| Scalability | Limited to SAP environment | Horizontally scalable |
| Tooling | SAP-native (PAL/AFL) | Open ML ecosystem (TensorFlow, LLMs) |
| Best For | Real-time process optimization | Cross-system intelligence & GenAI |
Example:
Embedded AI is ideal for in-line optimizations like smart defaults or lead time prediction.
Side-by-side AI excels in multi-system orchestration, AI-powered agents, or LLM integrations across channels.
3. SAP S/4HANA as a Reference Architecture
SAP S/4HANA enables both embedded and side-by-side AI models, making it a powerful example of intelligent ERP evolution.
✅ Embedded AI in SAP S/4HANA
- Built-in through SAP HANA and SAP AI Core
- Supports predictive and event-driven scenarios such as:
- Predictive lead times
- Intelligent approvals
- Situation handling via ML triggers
✅ Side-by-Side AI via SAP BTP
- Hosted on SAP AI Core, AI Foundation, or SAP Data Intelligence
- Allows integration with open-source ML libraries, GenAI platforms (e.g., OpenAI, LangChain)
- Supports AI Agents interacting with:
- IoT platforms
- CRM systems
- Third-party knowledge bases
4. Purpose and Value of This Analysis
This blog compared the embedded and side-by-side AI models in SAP S/4HANA.
Embedded AI is ideal for lightweight, in-system scenarios using SAP-provided libraries.
For complex AI workloads requiring neural networks and GPU-based processing, the side-by-side model via SAP BTPis preferred.
Both models leverage the Intelligent Scenario Lifecycle Management (ISLM) framework for standardized development and operations.
ISLM ensures consistent lifecycle management across AI use cases in SAP.
Together, these approaches enable scalable, intelligent automation within the SAP ecosystem.


Leave a comment